What is CBD (Cannabidiol)
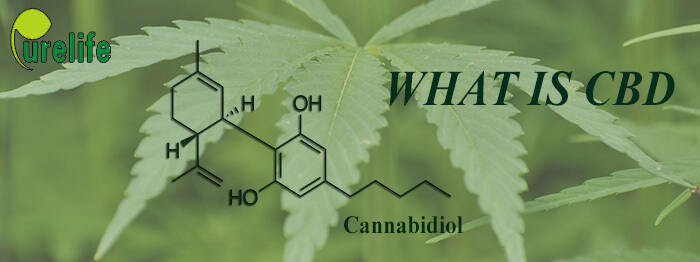
What is CBD
CBD, as known as Cannabidiol, is a type of cannabinoid, a chemical that’s naturally found in cannabis plants. The cannabis plant contains more than 100 different chemical compounds known as cannabinoids, such as :
- Cannabidiol(CBD)
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
- Anandamide
- Beta-Caryophyllene
Among these cannabinoids, THC and CBD are the most prevalent and the most well-understood.
Sources of cannabinoids
Marijuana is the main source of plant cannabinoids. In addition, the diet contains a variety of plant cannabinoids. For example, grapes, broccoli, cabbage, carrots, parsley, sunflower seeds, Cocoa, tea and peas all contain plant cannabinoids. Also, cooking herbs such as basil, cinnamon, black pepper, and rosemary all contain plant cannabinoids. Herbal medicine like echinacea, turmeric and licorice contain cannabinoids as well.
CBD benefits
Cannabidiol has the most medical value among the cannabinoids, it is a non-psychiatric active ingredient, and has a variety of pharmacological effects, including anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, stop vomiting and anti-inflammatory characteristics.
There’s plenty of anecdotal evidence that CBD helps treat a variety of ailments. People are turning to oils, gummies, and other Cannabidiol food and drink products to relax at the end of a long day. Retired NFL players are using Cannabidiol to manage physical pain, debilitating headaches, and sleeplessness. Spa clients are even using Cannabidiol skin products to fight signs of aging.
The main benefits of CBD include:
Pain Reliever
Researchers think that CBD (Cannabidiol) interacts with receptors in your brain and immune system. Receptors are tiny proteins attached to your cells that receive chemical signals from different stimuli and help your cells respond. This creates anti-inflammatory and painkilling effects that help with pain management. This means that Cannabidiol oil may benefit people with chronic pain, such as chronic back pain.
One 2008 review assessed how good CBD works to relieve chronic pain. The review looked at studies conducted between the late 1980s and 2007. Based on these reviews, researchers concluded Cannabidiol was effective in overall pain management without adverse side effects. They also noted that Cannabidiol was beneficial in treating insomnia related to chronic pain.
Stress and Anxiety
Cannabidiol may alleviate severe social anxiety.
In a 2011 study, scientists wanted to study the effects of CBD (Cannabidiol) on people with SAD(Generalized Social Anxiety Disorder). The scientists selected 24 people with this condition who had never received treatment for SAD then divided participants into two groups. One group received 600 mg of Cannabidiol while the control group received a placebo. The scientists then asked study participants to take part in a simulated public speaking test while researchers measured blood pressure, heart rate and other measurements of physiological and psychological stress.
The CBD group showed significantly reduced anxiety, cognitive impairment and discomfort in their speech performance. In comparison, those in the placebo group presented higher anxiety, cognitive impairment and discomfort.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 15 million adults in the United States have social phobia and about 6.8 million have a generalized anxiety disorder. Traditional treatment usually involves counseling and medications. Treatment with Cannabidiol may be better than anti-depressants because it acts quickly and does not cause side effects or withdrawal symptoms.
Anti-epileptic
As early as 2013, CNN broadcasted the story of Charlotte for the first time, which made CBD a hot spot around the world. Charlotte, who had severe muscular clonic epilepsy (Dravet syndrome), had 300 seizures per week every 15 minutes before treatment with Cannabidiol.
But after taking CBD oil, Charlotte’s seizures decreased significantly. After four months treatment, it only occurred once a week and now, Charlotte lives a normal life. Inspired by the Charlotte story, many epilepsy patients and their families around the world moved to Colorado for treatment, resulting in a rapid increase of 700 % in young epilepsy patients in the state.

Is CBD an addictive compound ?
Some people think that like THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD is an addictive compound, but as a matter of fact, CBD is not.
Among all of the cannabinoids in cannabis plants, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the only ingredient that has a powerful, intoxicating mental effect. THC stimulates the cells and results in dopamine release when it is in the brain. THC also activates your cannabinoid receptors, which have an impact on your brain in many ways. While some THC strains give you a burst of energy and creativity, the result is always a mellow feeling as the high takes over the body. It can cause hallucinations and delusions, and the immediate effects start within 10 to 30 minutes after THC consumption.
But CBD (Cannabidiol) is a Non-psychoactive compound, and it is not addictive. Multiple studies have shown that Cannabidiol is not toxic in non-converted cells, it does not induce systemic stiffness, does not affect physiological parameters (heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature), does not affect gastrointestinal transport, and does not change mental exercise or psychological function.
More importantly, CBD (Cannabidiol) can also reduce the mental stimulation of THC. THC binds directly to cannabinoid receptors in the body, but CBD does not bind well to the same cannabinoid receptor.
Side Effects of CBD
Immediate and long-term side effects of CBD appear to be minimal or inexistent, you may suffer after taking CBD are tiredness, diarrhea, and changes in your appetite or weight.
Not only CBD is non-psychoactive, but research has shown that it is non-toxic and there is no risk of lethal overdose. The study shown that long-term and high dose use (up to 1,500 mg/day) of CBD are still well-tolerated in human subjects.


