Product name : Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide(NAD)
Synonyms : beta-Diphosphopyridine nucleotide, beta-NAD,NAD,NAD+
CAS Number : 53-84-9
Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder
Specification : >99% purity (by HPLC)
MF:C21H27N7O14P2
MW:663.43

Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) review /What is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, also known as NAD, is the coenzyme form of the vitamin niacin. This coenzyme can be found in all living cells, it is s an abundant cofactor that participates in multiple aspects of cellular metabolism, which means NAD has many important roles for health, such as stimulating anti-aging activities of Sirtuins and the DNA damage repair enzymes.
What is the difference between NAD and NAD+
People always think that NAD is exactly the same as NAD+, but sorry, it is not correct.
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) exists in two forms: NAD+ and NADH. NAD+ is the oxidized form of NAD, and NADH is the reduced form of NAD.
NADH is produced in the glycolysis and Krebs cycle. It is essential to the chemical process for energy production. In glycolysis, two NADH molecules are produced per glucose molecule. Six NADH molecules are produced in the Krebs cycle per glucose molecule. These NADH molecules are used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP molecules.
NAD+ is an essential cofactor of key longevity enzymes called sirtuins, activating them directly. Sirtuins play a fundamental role in life expectancy as they deactivate particular genes that lead to ageing via inflammatory processes.
Thus the combined fall in sirtuins 1 and 3, and in NAD+, can cause cerebral degeneration, vascular inflammation, fatigue, loss of muscle strength, increased fat stores around the liver and abdomen and insulin resistance leading directly to metabolic syndrome.
Our bodies can produce NAD+ from a variety of different elements, but our levels of NAD+ drop significantly with age (as much as 50% as we get older).
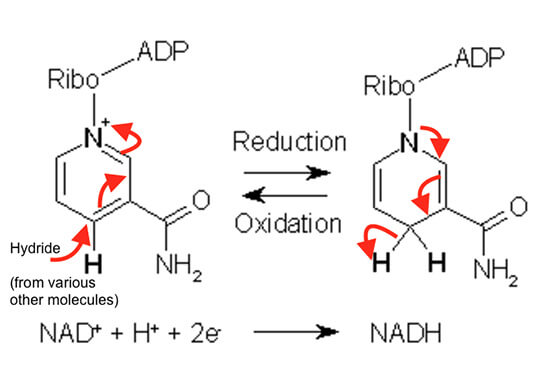
In a word, NAD+ and NADH are important co-enzymes in living cells, NAD+ is the oxidized form of NADH while NADH is the reduced form of NAD+.
How does Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) work ?
As we just said, NAD has an oxidized form as NAD+, and a reduced form as NADH. NADH converts nutrients into cellular energy (ATP), while NAD+ activates sirtuins, which makes our mitochondria healthier. Therefore, NAD+ has two general sets of reactions in the human body: helping turn nutrients into energy as a key player in metabolism and working as a helper molecule for proteins that regulate other biological activity. In short, NAD stimulates our sirtuins, slows down the deterioration of our mitochondria, which means a slower aging and a longer lifespan.
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) benefits/functions :
- Anti-Aging, enhance life-span
- Boost metabolism
- Improve Cognitive Brain Function
- Increase energy levels
- Lower blood/ cholesterol level
- Reduce Symptoms of Chronic Fatigue
- Preserve muscle mass and exercise capacity
- Support mitochondrial health
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) VS Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) VS Nicotinamide Riboside (NR)
NAD is a coenzyme found in all living cells, and vital to metabolism and hundreds of other biological processes.
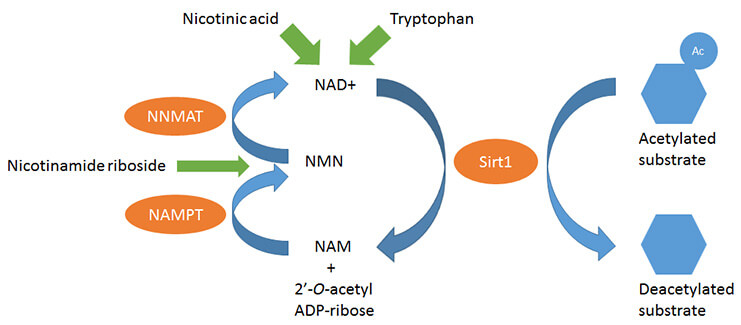
Both Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) are also called NAD precursor. What does this mean? It means that after we intake NMN or NR, both will be converted into NAD through a series of chemical transformations in the body first, then NAD will play a vital role in the body’s metabolism, and keep our body healthy. So the real thing our body need is NAD
NMN and NR effectively enhance NAD biosynthesis and have health benefits. In mammals, NMN is synthesized from nicotinamide by the rate-limiting enzyme, nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (NAMPT). NMN is also synthesized from NR via an NR kinase (NRK)-mediated phosphorylation reaction. NMN is then converted into NAD+ by NMN adenylyl transferases (NMNATs). NR is converted to NAD+ in a two-step process initiated by NRK, while the product of NRK is NMN.
NMN is more powerful, it is much faster than NR to metabolize to NAD, but as NMN is more difficult to synthesize, it is more expensive than NR
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) dosage
Generally, the recommended dosage of NAD is 2.5mg—20mg per day, but an appropriate dose depends on several factors such as the user’s age, health, and several other conditions. Please consult your dietitian for an appropriate dose before you supplement.
Where to buy Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
NAD level in our body declines dramatically as we age, which negatively impact our health. An appropriate supplement of NAD is necessary to keep our healthy. Purelife bio is a professional and reliable supplier of NAD and NAD precursors raw materials (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, Nicotinamide mononucleotide, Nicotinamide Riboside) with top quality. A timely and professional support will be provided upon your request.


