Product name : Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)

Synonyms : Beta-Nicotinamide mononucleotide, Beta-NMN, β-NMN,NMN, NAD+ Precursor
CAS Number : 1094-61-7
Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder
MF:C11H15N2O8P
MW:334.22
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) review /What is Nicotinamide mononucleotide?
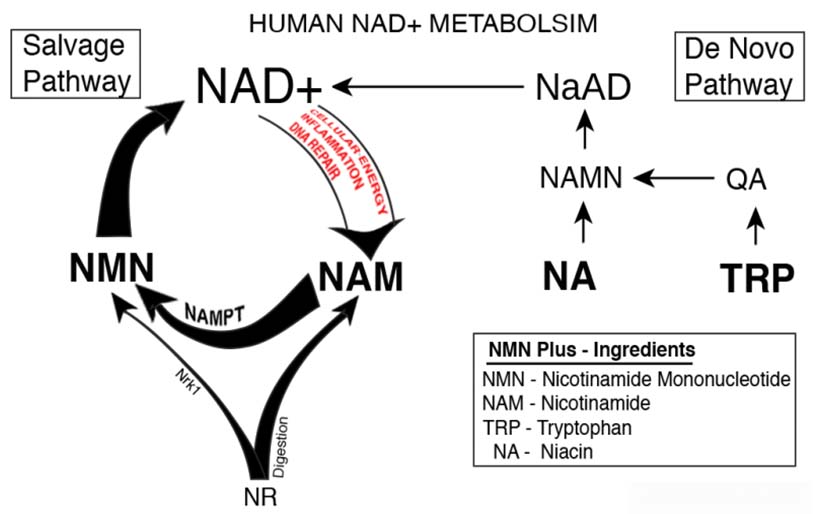
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is more and more popular now. It’s a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. Like nicotinamide riboside, NMN is a derivative of niacin, human body has enzymes that can use NMN to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
What is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is a coenzyme that consists of adenine and nicotinamide, it is found in every cell of all living organisms. NAD+ has been shown to be essential for supporting bodily functions by enhancing sensitivity, improving energy metabolism, and improving stress resistance. It also participates in genome protection through DNA repair, is neuroprotective, and is required for SIRTUIN activation.
NAD+ helps enzymes transfer electrons during redox reactions to form ATP and is thus an aid to energy supply. However, levels decline with age – the NAD+ in an older person’s cells falls by more than 50%, which means the mitochondria then produce less energy and cells age. But fortunately, this process is not irreversible and intercellular energy mechanisms can be restored if levels of NAD+ are increased.
In addition, NAD is an essential cofactor of key longevity enzymes called sirtuins, activating them directly. Sirtuins play a fundamental role in life expectancy as they deactivate particular genes that lead to ageing via inflammatory processes.
Thus the combined fall in sirtuins 1 and 3, and in NAD+, can cause cerebral degeneration, vascular inflammation, fatigue, loss of muscle strength, increased fat stores around the liver and abdomen and insulin resistance leading directly to metabolic syndrome.
Our bodies can produce NAD+ from a variety of different elements, but as we just said, our levels of NAD+ drop significantly with age. “NAD+ levels tend to drop by as much as 50% as we get older”, according to Dr. David Agus a world leading Physician in Cancer treatment and a pioneer in Biomedical Research.
How does Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) work ?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide is a product of eNAMPT (extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase) reaction and a key NAD+ intermediate. It ameliorates glucose intolerance by restoring NAD+ levels in HFD-induced T2D mice. It also enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity and restores gene expression related to oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and circadian rhythm, partly through SIRT1 activation
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) benefits/functions :
- Anti-Aging, enhance life-span
- Boost metabolism
- Improve Cognitive Brain Function
- Increase energy levels
- Management of healthy glucose levels
- Preserve muscle mass and exercise capacity
- Support Cardiovascular Health
- Support mitochondrial health
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or Nicotinamide Riboside (NR)? Which one is better?
According to the Washington University School of Medicine and associates Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Study, NMN takes 30 minutes to make its way through the liver, into muscle, and is metabolized to NAD+. NMN appears to be much faster than NR (Nicotinmide Riboside) which takes about 8 hours to reach peak NAD+ according to the study.
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) is converted to NAD+ in a two-step process initiated by NRK1, while the product of NRK1 is Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
So Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) would be better at boosting NAD+ levels .
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) Recommended dosage
The FDA suggests that a 150 pound (68kg) human would require about 560mg per day, and most branded NMN supplement shows 250mg daily , we suggest consulting a healthcare practitioner for proper dosage before you take .


